The Uno Minda Group is committed to creating sustainable value for all its stakeholders by integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into its business practices, including risk management. Including risk management As a leading global automotive component manufacturer, Uno Minda recognises that ESG factors have a significant impact on its long-term viability and success. In line with this commitment, Uno Minda has developed a robust business risk assessment strategy to identify, assess, and mitigate all foreseeable risks include ESG risks across its operations.
ESG factors also have become increasingly important in the business landscape, as investors, customers, and regulators demand greater transparency and accountability from companies. We recognise that addressing ESG risks is not only a matter of compliance but also a strategic imperative for sustainable growth and resilience in a rapidly changing world.
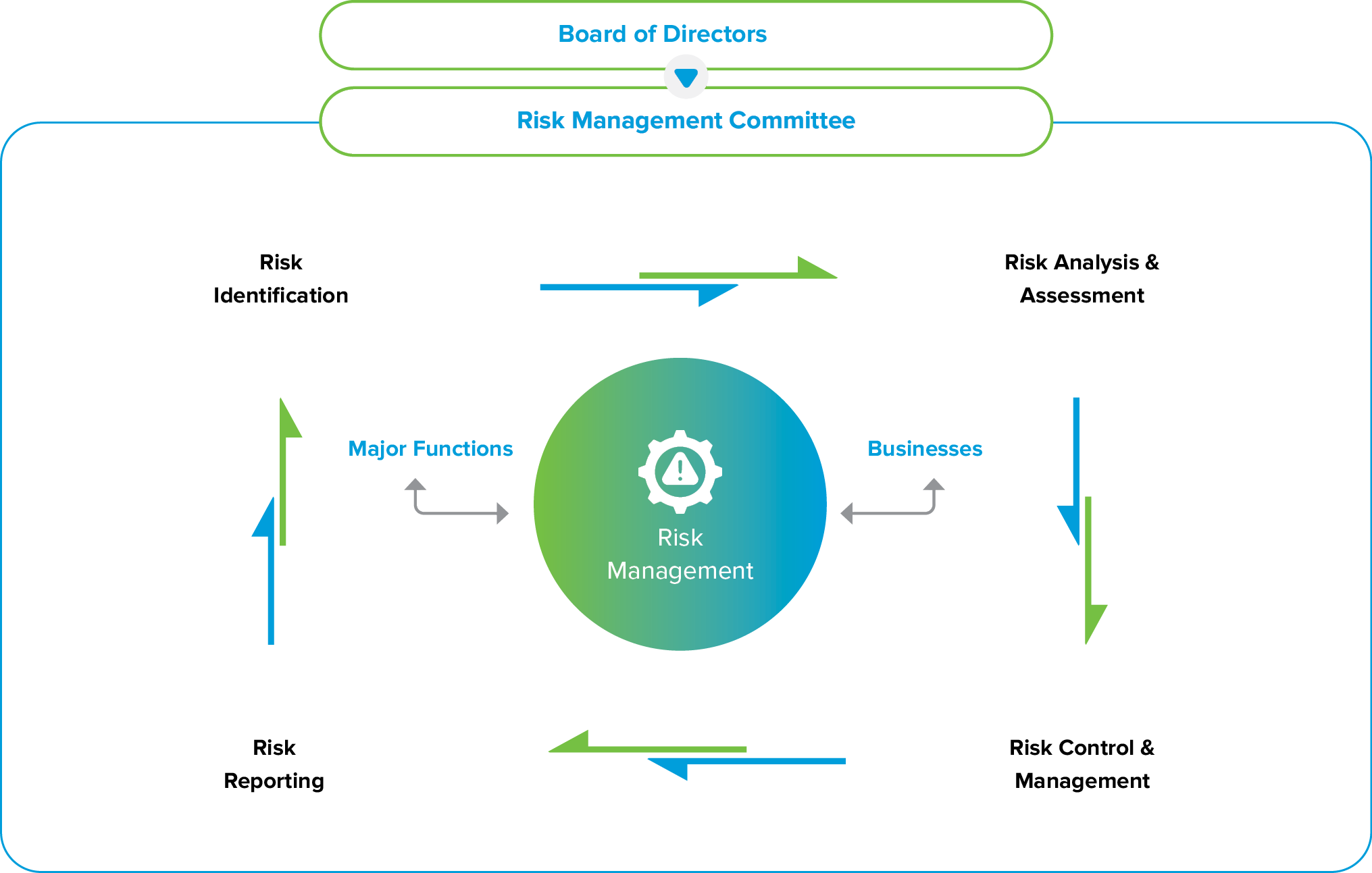
We have created an effective approach to risk management that allows us to effectively deal with existing and emerging risks while taking advantage on opportunities. Our risk governance design is led by the Risk Management Committee (RMC), which analyses our risk assessment and management approach on a periodic basis. Each department in our business participates in this process by identifying our most significant risks and indicating a mitigation strategy. Each realised risk is assigned a probability and an impact score, allowing us to categorise based on its sensitivity and the time frame within which it is expected to be identified. The effectiveness of each mitigation measure is examined on a regular basis based on the risk potential of each issue.
Risk areas we define are:
- Strategic Risk: A1 Business Geographies A2 Market and Technology Shifts
- Operational Risks: B1. Market Transitions B2 Sustainable Procurements Practices B3 Information management and security B4 Production processes B5 Delivery & Logistics B6 Product quality management
- Legal and Statutory Risks: C1 Compliance management
- Financial Risks: D1 Business Capital management D2 Taxes D3 International financial market
How We Assess Risk
Our risk assessment strategy encompasses a comprehensive framework that integrates ESG considerations into its risk management processes. This strategy enables the Company to identify potential ESG risks, evaluate their materiality and potential impact, and implement appropriate risk mitigation and ESG measures.
The key components of our business risk assessment strategy are as follows:

Risk Identification:We systematically identify and evaluates all risks including ESG risks across its value chain, encompassing its operations, supply chain, and stakeholder relationships. This includes risks related to natural calamities, resource scarcity, environmental pollution, labor practices, human rights, product safety, corporate governance and other operational risks.

Materiality Assessment:Once risks are identified, we conduct a materiality assessment to prioritise the most significant risks based on their potential impact on the Company’s operations and stakeholders. This assessment considers both the probability of occurrence and the potential magnitude of the risks.

Risk Evaluation: We conduct a thorough evaluation of the identified all risks including ESG risks, considering their potential financial, operational, reputational, and regulatory implications. This evaluation enables the Company to quantify and prioritise the risks based on their severity and potential consequences.

Risk Mitigation: After evaluating the risks, we implement appropriate risk mitigation measures to minimise their potential impact. This may involve implementing policies and procedures, setting targets and performance indicators, enhancing monitoring and reporting mechanisms, and engaging with relevant stakeholders to address specific risks.

Monitoring and Reporting:We continuously monitor the effectiveness of its risk mitigation measures and reports on its progress. The Company discloses relevant ESG information to its stakeholders through integrated sustainability reports, which provide a transparent account of its ESG performance, initiatives, and goals.
Risk Assessment Matrix
We have an all-encompassing risk management policy and use both a top-down and bottom-up approach to risk management. Risk assessment is conducted taking understanding of two aspects: the amount of implication the risk can cause to the business on an annual basis and its probability of occurrence in the ecosystem Each risk is graded as extremely low, medium, or high based on the nature and extent of the implication. The likelihood of occurrence is calculated using percentages and categorised as unlikely to happen, feasible, likely to happen, and extremely likely to happen. The risk class is determined by the combination of the expected amount of implications and the probability of occurrence, which can be low, medium, or high depending on the impact on business, assets and finances.
Risk Mitigation Strategy
| Key Risk | Description of Risk | Risk Mitigation Strategy | Impacted Capitals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pandemic/calamities |
The pandemic-induced lockdown resulted in the shutting down of production at all the OEMs. It also led to the disruption of the entire value chain of major industries in India, and therefore negatively affected the production of auto components as well Repeated stance of the Covid-19 pandemic induced waves may force the Government to introduce strict lockdown-like measures. These may have an adverse impact on the regular operations and sales of the Company. |
The Company continuously and closely monitors the developments and possible effects that may result from pandemic like situations or calamities on its financial condition, liquidity and operations and actively works to minimise the impact of such unprecedented situations. | Social and Human |
| Market and Technology Shifts |
There have been marked policy shifts towards decarbonisation i.e., shift from carbon-based fuels to clean energy. The changing demands from the costumers to adopt to these changes has been on rise. Since this requires both approach and technological shift from current production capacities, the risk of reduction in value creation and market contribution is higher. |
We are taking varied proactive measures to adopt these changes in market and customers’ mindsets. There have been changes in production lines and systems, types of products being offered and emergence of modular offerings. We are diligently working on improving our work efficiencies, product qualities and range of products to address the ever increasing demands in the market. | Financial, Manufacturing, Intellectual, Social and Relationship |
| Geopolitical |
Geopolitical risks such as war outbreaks, government instability, social unrest, the rise of nationalism and populism and disputes between sovereign states may result in acute supply chain disruption and impact the production levels of the Company. |
The Company keeps on exploring options for sourcing products from multiple vendors strategically located in different geographies. Further, regular efforts are made towards localisation as well. | Financial, Manufactured |
| Sustainable Procurement Practices |
Procurement risks arise mainly due to raw materials price fluctuations, and an insufficient supply of raw material, among others. This could itself be a result of various factors like the economic cycle, and political instability. Adverse fluctuations in market prices and/or a supplier’s financial distress could have an impact on the Company’s financial position and earnings. |
The Company’s purchasing function ensures optimal supply of goods and services to the Company, focusing on quality, cost, and delivery performance. Options for multiple product sourcing and localisation are continuously explored. By negotiating prices and utilising economic synergies, the Company is largely able to obtain competitive prices. The Company recognises that sustainable procurement practices are vital for promoting environmental responsibility, social well-being, and long-term business sustainability. We conduct assessments of our supply chain partners to evaluate their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices. We have established a comprehensive Supplier Code of Conduct that outlines our expectations regarding human rights, labour standards, environmental protection, and business ethics. The Company encourages its suppliers to adopt sustainable practices, and work towards reducing carbon emissions, water usage, waste generation, and other key environmental indicators. |
Financial, Manufacturing, Social and Relationship |
| Information Management and Security |
Considering the connectedness of geographies and businesses, we may face operational risks related to data breaches, cyberattacks, or unauthorised access to sensitive information. Such incidents can result in the loss, theft, or compromise of valuable data, including confidential business data. This includes challenges in data classification, access controls, data retention, compliance with data protection regulations, or inadequate safeguards for sensitive information. Lack of employee awareness and training on information security best practices can increase operational risks. Human errors, such as clicking on phishing emails or mishandling sensitive data, can inadvertently expose the Company to cyber-security threats and data breaches. |
The Company has the highest standards of IT security systems and constantly upgrades the IT security infrastructure. We have implemented comprehensive policies, procedures, and controls to safeguard sensitive data and prevent unauthorised access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. We employ role-based access controls, strong authentication mechanisms, and regular access reviews to minimise the risk of unauthorised access or internal threats. We also conduct regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing to identify and remediate any potential weaknesses. We invest in ongoing awareness programmes and training to educate employees about their responsibilities, best practices, and emerging threats related to information security. By promoting a culture of security awareness, we empower our employees to identify and report potential security incidents, reducing the risk of human error or negligence. | Financial, Manufacturing, Intellectual, Human, Social and Relationship |
| Production Processes |
As the Company’s manufacturing facility is capital-intensive, a large proportion of its costs are fixed. As a result, a decrease in the utilisation of plant capacity leads to under absorption of costs and thereby adversely impacts its earnings. Moreover, the influence of force majeure could result in delays or interruptions of production and supply chain, leading to non-fulfillment of market demand. Risks can arise from inefficiencies or suboptimal utilisation of resources in production processes. These risks include wasted materials, energy inefficiencies, production bottlenecks, and reduced overall productivity. |
The Company regularly reviews market conditions and aligns its production plan accordingly. The Company’s good relations with its customers and suppliers further help it to estimate and pile up inventory levels at both side procurement and manufacturing. The Company places a strong emphasis on maintaining high-quality standards throughout the production processes. We have implemented robust quality control measures, including regular inspections, testing, and process monitoring, to ensure that our products meet or exceed customer expectations. Through the adoption of lean manufacturing principles, advanced technologies, and data-driven decision-making, the Company constantly seeks to optimize its processes, increase efficiency, and reduce waste. The Company invests in comprehensive training prpgrammes to enhance the skills and knowledge of its workforce. By equipping our employees with the necessary tools and expertise, the Company strives to minimise human errors, improve operational efficiency, and promote a culture of safety and continuous improvement |
Manufacturing, Financial |
| Competition |
The markets for auto components are rapidly evolving and highly competitive, and it is expected that competition will continue to intensify. The Company faces competition in all business fields it operates in. As a result, the Company is exposed to the dual risk of either getting displaced by existing or new competitors or having its products replaced by product innovations or by new technological features. Customer dissatisfaction with price, quality, delivery performance and design could lead to a loss of market share. |
The Company ensures close cooperation with its key customers on product development. It has implemented strict product quality controls in order to reduce the likelihood of substitution. The Company is also developing products that will help it to step up the value chain while building a robust product portfolio. |
Financial, Manufacturing, Social and Relationship |
| Product Quality Management |
We understand the risk of producing and delivering defective products that do not meet the required quality standards. This includes issues such as manufacturing errors, component failures, design flaws, or deviations from specifications. Failure to meet these standards can result in product recalls, legal liabilities, fines, or damage to the Company's reputation. |
We have implemented robust quality control systems throughout our operations. These systems encompass comprehensive inspection, testing, and monitoring processes at various stages of the production cycle. We have also implemented stringent supplier selection criteria and actively collaborate with our suppliers to ensure adherence to our quality standards. |
Financial and Social |
| Compliance Management |
There is always a risk of failing to comply with applicable laws, regulations, and statutory requirements. This includes risks related to labour laws, environmental regulations, health and safety standards, taxation, trade compliance, data protection, and other legal and statutory laws and regulations. |
The Company has established a robust compliance framework to ensure adherence to all applicable laws, regulations, and statutory requirements. The compliance management system is designed to identify, assess, and mitigate legal and statutory risks across our operations. Our dedicated compliance team stays updated on regulatory developments and assesses their potential impact on our business. This proactive approach allows us to anticipate changes, adapt our processes accordingly, and ensure continued compliance with evolving legal and statutory requirements |
Financial, Manufacturing, Intellectual, Social and Relationship, Human |
